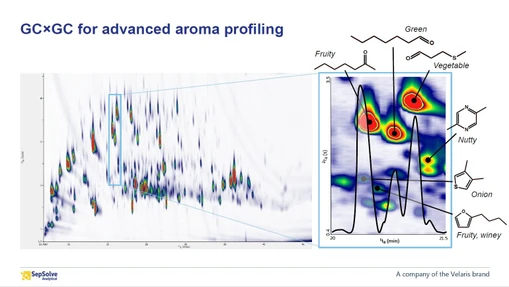
Application of GC×GC for the investigation of fermented beverages (Sarah C. Foster, MDCW 2026)

- Photo: MDCW: Application of GC×GC for the investigation of fermented beverages (Sarah C. Foster, MDCW 2026)
- Video: LabRulez: Sarah Foster: Application of GC×GC for the investigation of fermented beverages (MDCW 2026)
🎤 Presenter: Sarah C. Foster (William & Mary)
Abstract
Fermentation is a byproduct of microbial metabolism. When beverages become fermented, the microorganisms involved produce volatile organic compounds (VOCs). It is important to examine the VOC profile of fermented beverages to understand their consumer perception and health considerations. Traditionally, VOCs are detected by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). However, more complex matrices, like fermented products, benefit from the enhanced separation of comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography (GC×GC). This study aimed to develop an understanding of the VOCs related to different fermented beverages through a nontargeted lens via comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with dual detection using flame ionization detection and time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC×GC-FID/TOFMS).
Data analysis focused on developing a complete VOC profile of fermented products. Moreover, analysis aimed to identify differentiating VOCs to understand differences between products and distinguish the drink matrix from the microbial matrix. Results indicate that it is possible to attribute VOCs to one component of a complex sample, creating a microbial VOC profile and a base VOC profile. It was possible to discern products from one another, including contaminated products from non-contaminated products. Data visualization consisted of Principal Component Analysis (PCA) scores and loadings plots, bar chats, Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA), and Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA). Data analysis software was capable of processing and aligning samples with high levels of biological variation, making GC×GC a promising analytical tool for market research and regulation. Future studies will aim to correlate VOCs detected via GC×GC-FID/TOFMS to the microbial genetics of fermented products.
Video Transcription
1. Introduction
Sarah Foster introduces research focused on the application of comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography (GC×GC) for analyzing fermented beverages.
The laboratory primarily uses GC×GC for:
- Separation and identification of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
- Applications in forensic sciences and food sciences
Forensic Applications
- Fingerprint residue
- Gunshot residue
- Pepper spray
- Other trace evidence
Food Science Applications
- Fermented beverages
- Foods claiming health benefits
An additional focus of the lab is transitioning GC×GC from proof-of-concept research toward real-world field applications, including improved data interpretation and presentation.
2. Challenges in Non-Targeted GC×GC Data
Working with complex, non-targeted datasets presents several challenges:
- Resolution of complex coelutions
- Increased number of detectable features
- Expansion of compound classes
- Detection of low-level analytes previously masked by abundant compounds
- Difficulty in longitudinal tracking due to increased data complexity
While GC×GC reveals more chemical information, interpreting this data becomes more demanding.
3. Data Processing and Statistical Tools
Software Used
- ChromaTOF – for single chromatogram peak detection and deconvolution
- ChromaTOF Sync 2D – alignment software for entire datasets
- R statistical software – for multivariate visualization
- vegan package
- ComplexHeatmap package
Advantages of Sync 2D
- Performs peak detection and deconvolution across all chromatograms simultaneously
- Generates a unified peak table for entire datasets
- Facilitates trend analysis
Dimensionality Reduction Techniques Used
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCoA)
- Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA)
Each data point includes:
- Primary retention time
- Secondary retention time
- Signal intensity
4. Statistical Approaches Explained
PCA (Principal Component Analysis)
- Uses Euclidean distance
- Assumes linear variance structure
- Clustering based on shared analytes
- Identifies key analytes driving variance
- Loadings plots explain separation patterns
PCoA (Principal Coordinate Analysis)
- Uses non-Euclidean dissimilarity (e.g., Bray–Curtis)
- Emphasizes compositional differences
- Better for non-linear variance structures
HCA (Hierarchical Cluster Analysis)
- Uses Euclidean dissimilarity (in this study)
- Clustering based on:
- Presence/absence
- Relative abundance
- Output: dendrogram
- Short branches = more similar
- Long branches = more dissimilar
5. Research Goals
- Apply GC×GC-TOFMS for volatile analysis and aroma profiling of mead
- Investigate impact of:
- Yeast strain
- Honey concentration
- Use a non-targeted analytical approach
- Extract and compare chemical features across samples
6. Mead Production Overview
Mead is produced by fermenting honey with filtered water. Fruits or spices may be added. It may also be barrel-aged.
Experimental Design (Silverhand Meadery Collaboration)
- 1-gallon batches
- 5 yeast strains
- 3 honey concentrations:
- 1.5 lb/gal (low alcohol, expected dry finish)
- 3 lb/gal (standard)
- 5 lb/gal (high alcohol, expected sweet finish)
Yeast Strains Tested
- Kveik Voss – neutral with citrus notes
- Munich – banana, clove (esters & phenols)
- EC1118 – neutral (sparkling wine yeast)
- D47 – tropical/white floral
- Abbaye – temperature-dependent:
- Low temp: banana, tropical, spicy
- High temp: raisin, fig
Fermentation lasted 9 months. Stabilizers were added post-fermentation.
7. Sample Preparation
Mead Samples
- 3 mL in 20 mL headspace vial
- 0.5 g salt
- 5 µL (500 ppm) 1-decanol internal standard
Honey Samples
- 1.5 g honey + 1.5 mL water
- Salt + internal standard
Water Controls
- 3 mL water + salt + internal standard
All samples were vortexed and analyzed by GC×GC-TOFMS.
8. Instrumentation
Instrument: LECO Pegasus BTX 4D GC×GC-TOFMS
Features:
- Dual TOFMS and FID detection
- Reverse fill/flush modulator
- Flow splitter
The modulator:
- Fills loop in forward direction
- Flushes to secondary column
- High secondary flow split between TOFMS and FID
9. Initial Observations
Key compounds identified:
- Furfurol (heated honey marker)
- 2-ethylhexanol (water)
- 3-methylbutanol (fermentation product)
- Benzaldehyde (fermentation product)
Total detected: 96 volatile organic compounds
10. Multivariate Results
PCA Findings
- Four groupings largely dictated by honey concentration
- 1.5 lb/gal group clustered together
- 3 lb/gal group tightly clustered
- 5 lb/gal showed pattern similar to 1.5 lb/gal
- Abbey yeast formed a distinct cluster
PCoA Findings
- Similar overall patterns
- Abbey yeast more distinctly separated
- Likely due to Bray–Curtis dissimilarity emphasizing compositional differences
HCA + Heatmap Findings
- Clustering aligned with PCA/PCoA trends
- Abbey yeast again formed distinct grouping
- Appeared to contain similar compounds but in lower relative abundances
Two major overall clusters:
- 1.5 lb/gal group
- All other meads
11. Compound Trends vs Honey Concentration
Observed correlations:
- Ethyl lactate: increased with honey concentration
- Furfurol: increased with honey concentration
- 3-methylbutanol:
- Decreased with honey concentration (except Abbey strain)
- Ethyl octanoate:
- Highest at 3 lb/gal
- Lowest at 1.5 lb/gal
- Intermediate at 5 lb/gal
Abbey strain showed unique behavior, possibly explaining its distinct clustering.
12. Conclusions
- GC×GC-TOFMS is highly effective for aroma profiling of mead
- Dimensionality reduction techniques successfully highlighted relationships between samples
- Honey concentration strongly influences volatile profile
- Yeast strain (especially Abbey) significantly impacts composition
13. Future Work
- Investigate microbial environment effects on VOC production
- Link microbial kinetics data to volatile profiles
- Explore compound-class-specific trends
This text has been automatically transcribed from a video presentation using AI technology. It may contain inaccuracies and is not guaranteed to be 100% correct.
-Workshop-LOGO_s.webp)