Pesticide Residue Analysis in the 21st Century: Innovations in Sample Preparation and Detection Using the Thermo Scientific TSQ 9610 GC-MS/MS

- Photo: Thermo Fisher Scientific: Pesticide Residue Analysis in the 21st Century: Innovations in Sample Preparation and Detection Using the Thermo Scientific TSQ 9610 GC-MS/MS
- Video: Chromatography & Mass Spectrometry Solutions: TSQ 9610 Triple Quadrupole GCMSMS System
Introduction
The accurate detection of pesticide residues in food and environmental matrices is essential for regulatory compliance and public health protection. With increasingly stringent maximum residue levels (MRLs), modern laboratories must rely on highly sensitive, robust, and efficient analytical workflows.
 Thermo Fisher Scientific: Pesticide Residue Analysis in the 21st Century: Innovations in Sample Preparation and Detection Using the Thermo Scientific TSQ 9610 GC-MS/MS.
Thermo Fisher Scientific: Pesticide Residue Analysis in the 21st Century: Innovations in Sample Preparation and Detection Using the Thermo Scientific TSQ 9610 GC-MS/MS.
The Thermo Scientific TSQ 9610 triple quadrupole GC-MS/MS system represents a significant advancement in targeted multi-residue pesticide analysis, combining advanced ionization, automation-ready design, and flexible sample preparation compatibility. This blog explores the scientific foundation and practical advantages of the Thermo Scientific TSQ 9610 in conjunction with contemporary preparation techniques such as QuEChERS and Automated μSPE Solid Phase Extraction for GC and LC-MS.
Evolution of pesticide residue sample preparation
1. Historical context
Early pesticide analysis, up to the 1950s, relied on labor-intensive liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) techniques using solvents like petroleum ether, chloroform, and acetone. These methods were time-consuming, lacked selectivity, and produced poor recovery for trace-level compounds.
2. The chromatographic era
The introduction of gas chromatography (GC) in the mid-20th century revolutionized pesticide detection. The use of solid-phase clean-up (e.g., Florisil®, silica gel), derivatization steps, and the first electron capture detectors (ECD) significantly enhanced sensitivity for halogenated compounds.
3. Solid phase extraction and HPLC integration
In the 1980s, solid-phase extraction (SPE) emerged as a faster and more selective alternative to LLE. It facilitated cleaner extracts with reduced solvent usage. Simultaneously, HPLC became essential for analyzing thermally labile compounds not suitable for GC.
4. Multiresidue methods and mass spectrometry
The 1990s saw the development of standardized multi-residue methods (e.g., DFG-S19 in Germany), enabling the simultaneous quantification of dozens of pesticides. Coupling with GC-MS and later LC-MS/MS provided both structural confirmation and improved sensitivity.
QuEChERS and the rise of simplified extraction
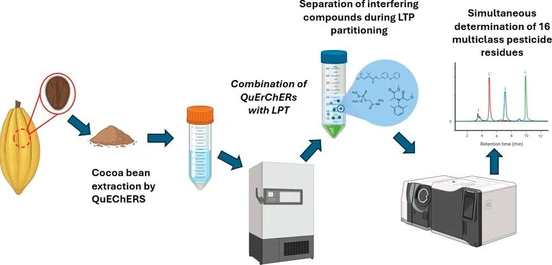
Introduced by Anastassiades et al. in 2003, the QuEChERS (Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged, Safe) method revolutionized sample preparation. Based on acetonitrile extraction, salting out partitioning, and dispersive SPE (d-SPE), it became the de facto standard for regulatory testing of fruits, vegetables, grains, and more.
Benefits of QuEChERS include:
- Minimal equipment and solvent use
- High recoveries for a wide polarity range
- Compatibility with both GC-MS/MS and LC-MS/MS
However, challenges remain, especially for high-fat or pigmented matrices, where residual co-extracts can suppress analyte response and contaminate instrumentation.
Micro-SPE: precision clean-up for modern workflows
Micro solid-phase extraction (µSPE) is a miniaturized evolution of SPE, optimized for post-QuEChERS clean-up:
Scientific Advantages:
- Higher selectivity with tailored sorbent chemistries
- Improved elution profiles due to smaller particle sizes
- Reduced dead volume, minimizing solvent and analyte loss
- Online compatibility with autosamplers and injection systems
In a study by Hakme and Poulsen (2021, J. Chromatogr. A), µSPE was shown to remove over 70% of matrix interferences in cereal samples compared to d-SPE, significantly improving downstream MS performance.
TSQ 9610 GC-MS/MS: designed for demanding applications
1. AEI ion source
The Advanced Electron Ionization (AEI) source generates a tightly focused ion beam, yielding exceptional signal intensity and stability—even with matrix-heavy samples. Its robust construction reduces maintenance cycles while maintaining low detection limits.
2. XLXR detector
This new detector architecture provides an extended linear dynamic range, allowing the quantification of analytes from low-ppt to high-ppb levels in a single run—critical for screening both regulated and emerging contaminants.
3. NeverVent technology
Instrument uptime is maximized with Vacuum Probe Interlock (VPI), enabling:
- Column exchange
- Ion source replacement
- without system venting, preserving vacuum integrity and reducing downtime.
4. Integrated backflush capability
The system’s intelligent backflush mechanism allows:
- Faster matrix removal
- Reduced contamination of the analytical column
- Enhanced peak shape and reproducibility
Carrier gas considerations: Hydrogen vs. Helium
With rising helium costs and supply concerns, hydrogen is gaining popularity as a carrier gas for GC-MS/MS. While hydrogen introduces changes to ionization efficiency and fragmentation patterns, method optimization can mitigate these effects.
Example:
Deltamethrin, Pentachlorobenzene, and Isodrin were all successfully quantified at 0.005 mg/kg in baby food using hydrogen, with comparable signal-to-noise ratios to helium-based methods.
Note: SRM transitions may need to be re-optimized due to altered ion ratios under hydrogen conditions.
Application spotlight: cereal matrix validation
In a validation study across five cereal matrices (wheat, rice, barley, rye, oats), µSPE provided:
- Matrix removal >70%
- Clean chromatograms
- Stable quantification at sub-ppb levels
This demonstrates the system’s applicability to routine food safety testing, even in complex and variable sample types.
Conclusion
The combination of advanced sample preparation techniques and the cutting-edge Thermo Scientific TSQ 9610 GC-MS/MS system provides laboratories with a future-ready platform for pesticide residue analysis. Whether tackling routine compliance or challenging research applications, this integrated solution ensures:
- Enhanced matrix removal
- Low detection limits
- Robust, reproducible results
- Flexibility in sample types and carrier gas usage
Further information:
- Contact me at [email protected]
- Free webinar in German language
- On-demand webinar in English language
- Visit us on LinkedIn: #GC-MS/MS #Pesticides #SamplePreparation #HyrogenCarrierGas
Petra Gerhards
Petra Gerhards, Dipl-Ing, is Regional Marketing Manager of GC and GC-MS for EMEA at Thermo Fisher Scientific. She has more than 29 years of experience in the fields of GC-MS, SPE and LC-MS. Since joining the regional team she has contributed to workflow solutions combining vials and closures with SPE solutions, GC-MS and LC-MS. She works with KOL's on data for regional specific marketing campaigns, organizes in-house seminars and works on customer specific solutions. Her main expertise is in the field of doping and drugs-of-abuse analysis.