A Single Calibration Method for Water AND Soil Samples Performing EPA Method 8260

- Photo: EST Analytical: A Single Calibration Method for Water AND Soil Samples Performing EPA Method 8260
- Video: EST Analytical: EST CENTURION | EST Analytical
Abstract
Environmental laboratories are always searching for techniques to increase productivity. However, environmental methods demand a large amount of background information in order to ensure sampling and analysis is compliant. The determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) in the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) Method 8260 encompasses many different matrices and in doing so has numerous sampling, quality control, and calibration requirements. The matrices of Method 8260 samples can also vary from air to sludge and from clean to extremely contaminated. Furthermore, the method has an extensive calibration range. All of these factors play into the complexity of sampling and analysis thus, creating ways to streamline sampling while still maintaining sample integrity and method compliance is always of interest to environmental laboratories.
Introduction
In order to run Method 8260 samples, a bromofluorobenzene (BFB) tune standard, matrix blank, calibration standard, and laboratory control standard all have to be run and pass method requirements every twelve hours. With the exception of the BFB standard, the other standards and blank matrices have to correspond to the samples to be analyzed. Due to this constraint, the analyst is required to run another three samples if the matrix is changed within the twelve hour time window. Moreover, the calibration must also match the sample matrix. These requirements are very time consuming and can limit laboratory profits. This application note will demonstrate a patented automated water sampling mode using the soil sampling station of the autosampler thus eliminating the need to have separate calibrations and standards for waters and soils.
Discussion
There are a number or techniques that can enable an analyst to save time in an environmental lab. Analysts can decrease analytical trap bake times, change sample purge time and flow, utilize a dual sampling system for one GC/MS, etc. However, one of the most basic ways to save time is by reducing the number of required curves and standards needed.
EST Analytical has designed a patented, automated water sampling mode that will allow environmental laboratories to run water samples in the soil mode. Thus, water and soil curves, standards, blanks and samples can use the same sampling parameters. (See steps 1, 2, and 3 below). This innovative sampling mode would eliminate the need to have separate curves, standards, etc. for soils and waters, thus saving laboratories time and money. Please note that this procedure may only be used with auditor approval.
 EST Analytical: Sampling
EST Analytical: Sampling
Experimental
The sampling system used for this study was the EST Analytical Centurion WS autosampler and Evolution concentrator. The concentrator was affixed with a Vocarb 3000 trap and connected to an Agilent 7890A GC and 5975 inert XL MS. The GC was configured with a Restek Rxi-624 Sil MS 30m x 0.25mm x 1.4µm column. The experiments were run using the extraction mode of the Centurion WS. Sampling method parameters and GC/MS parameters are listed below.
Purge and Trap Parameters
- Concentrator: EST Evolution
- Trap type: Vocarb 3000
- Valve oven temperature: 150 °C
- Transfer line temperature: 150 °C
- Trap temperature: 35 °C
- Moisture Reduction Trap (MoRT) temperature: 39 °C
- Purge time: 11 min
- Purge flow: 40 mL/min
- Dry purge Temp.: Ambient
- Dry Purge Flow: 40mL/min
- Dry Purge Time: 1.0 min
- Desorb pressure Control: ON
- Desorb Pressure: 5psi
- Desorb time: 0.5 min
- Desorb preheat delay: 5 sec
- Desorb temperature: 260 °C
- MoRT bake temperature: 230 °C
- Bake temperature: 270 °C
- Sparge vessel bake temperature: 120 °C
- Bake time: 8 min
- Bake flow: 40 mL/min
Auto-Sampler (EST Centurion WS):
- Sample type: Water Extraction
- Sample Fill Mode: Syringe
- Sample Volume: 10mL
- IS Volume: 5µl
- Needle Rinse Time: 20 sec
- Needle Sweep Time: 20 sec
- Concentrator Desorb Time: 0.5 min
- Syringe Rinse: On/12mL
- Number of Syringe Rinses: 2
- Sparge Rinse Time: Off
- Water Heater Temp.: 85°C
GC/MS Parameters
- System: Agilent 7890/5975 inert XL
- Inlet: Split mode, 200 °C, 40:1 split ratio, 12.153 psi head pressure
- Column: Restek Rxi-624Sil MS, 30 m × 0.25 mm × 1.4 µm
- Oven program: 45 °C (1 min) → ramp 15 °C/min → 220 °C, hold 1.3 min
- Column flow rate: 1 mL/min helium
- Total flow: 44 mL/min
- Source temperature: 230 °C
- Quadrupole temperature: 150 °C
- Transfer line temperature: 180 °C
- Scan range: m/z 35–265, 3.12 scans/sec
- Solvent delay: 0.7 min
The USEPA Method 8260 standards were acquired from Restek. The linear range of the water extraction experiment was established by running a nine point calibration curve with a range of 0.5 to 200ppb. Method detection limits were also established for each compound by examining seven replicate standards of the low calibration point. Finally, precision and accuracy were determined by running seven replicate midpoint standards. Figure 1 displays a 50ppb Method 8260 standard chromatogram of a water sample run in soil mode and experimental results are listed in Table 1.
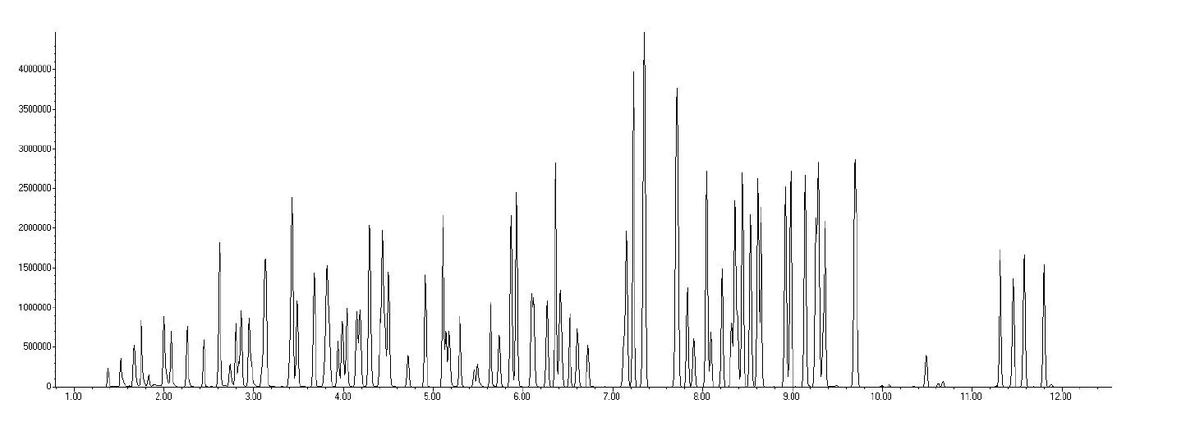 EST Analytical: Figure 1: 50ppb Chromatogram of a Water Sample Run in Soil Mode
EST Analytical: Figure 1: 50ppb Chromatogram of a Water Sample Run in Soil Mode
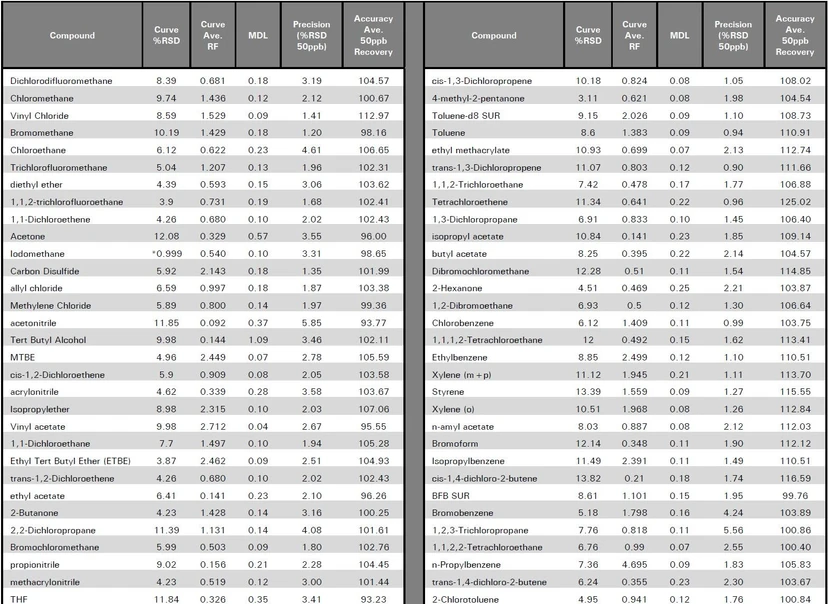 EST Analytical: Table 3: Experimental Results_part 1
EST Analytical: Table 3: Experimental Results_part 1
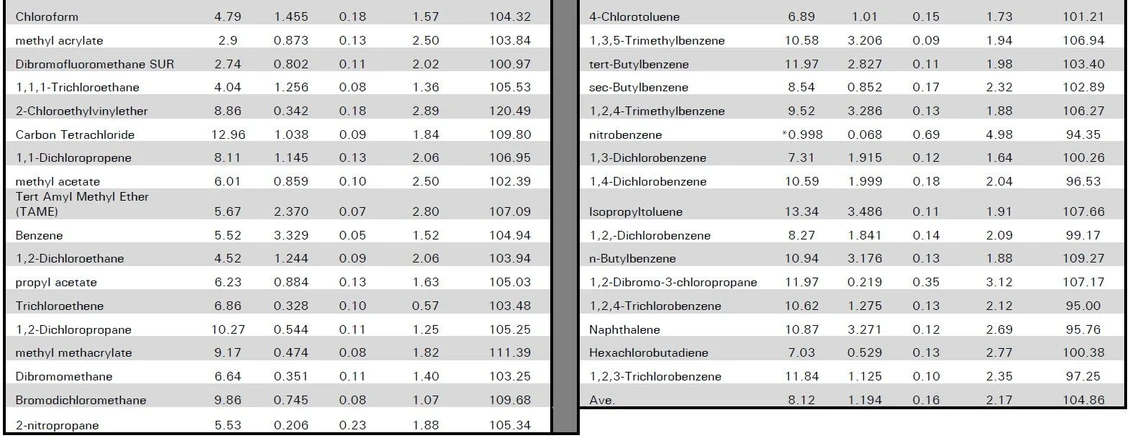 EST Analytical: Table 3: Experimental Results_Part 2
EST Analytical: Table 3: Experimental Results_Part 2
Conclusion
The patented sampling process of the Centurion WS proved to be a reliable and accurate sampling method for running water samples in the soil mode. The curve linearity and method detection limits both met USEPA Method 8260 requirements, and the precision and accuracy results were excellent. The water extraction option offered with the Centurion WS will save laboratories time and money because only one set of standards, curves, etc. is required for both water and soil samples.
- Volatile Organic Compounds by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS); United States Environmental Protection Agency Method 8260B, Revision 2, December 1996.