A fast thermal desorption unit for micro thermal desorption tubes, Part I: Development of the system and proof of concept measurements with hyper-fast gas chromatography

Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1730, 2024: A fast thermal desorption unit for micro thermal desorption tubes, Part I: Development of the system and proof of concept measurements with hyper-fast gas chromatography
The goal of this study is to design and validate a novel thermal desorption unit (TDU) paired with micro thermal desorption tubes (TD-tubes) for rapid analyte desorption in hyper-fast gas chromatography. By reducing the thermal mass of the TD-tubes, the system achieves extremely fast heating and cooling cycles, enabling thermal desorption within 12 seconds and a cycle time of 90–100 seconds.
The study investigates the impact of TD-tube dimensions on critical parameters such as desorption time, breakthrough volumes, porosity, linear velocity, and back pressure. Proof of concept demonstrates excellent precision and linearity in analyzing n-alkane mixtures using flow-field thermal gradient gas chromatography (FF-TG-GC), highlighting the system's potential for efficient, high-speed analytical applications.
The original article
A fast thermal desorption unit for micro thermal desorption tubes, Part I: Development of the system and proof of concept measurements with hyper-fast gas chromatography
Miriam D. Chopra, Florian A. Menger, Benny Duong, Matthias Wüst, Peter Boeker
Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1730, 16 August 2024, 465039
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2024.465039
licensed under CC-BY 4.0
Selected sections from the article follow. Formats and hyperlinks were adapted from the original.
Highlights
- New micro thermal desorption tubes (μTD-tubes) for fast GC analysis.
- Rapidly heatable and coolable thermal desorption unit for μTD-tube desorption.
- Low thermal mass μTD-tubes and thermal desorption unit.
- New application for flow field thermal gradient gas chromatography (FF-TG-GC).
- Fast thermal desorption of n-alkanes within 12 s and a cycle time of 90 – 100 s.
- Impact of μTD-tube dimensions on a.o. breakthrough, porosity and linear velocity.
Abstract
A system consisting of a thermal desorption unit (TDU) and micro thermal desorption tubes (μTD-tubes, 1.4 mm I.D., 10 mg Tenax TA) for fast desorption of analytes was developed for the efficient combination of hyper fast gas chromatography with thermal desorption. The fast desorption is achieved by a significantly reduced thermal mass compared to conventional thermal desorption tubes. Therefore, extremely fast heating and cooling cycles are possible. Proof of concept measurements combining the new setup with a flow-field thermal gradient gas chromatograph (FF-TG-GC) and FID detection show good precision and linearity with R2 ≥ 0.995 in the analysis of an n-alkane mix (C8 - C20). Thermal desorption occurs within 12 s. The impact of reduced μTD-tube dimensions on desorption time, full width at half maximum (FWHM), breakthrough volumes, tube flow rates ergo linear velocities, porosity and back pressure is discussed.
1. Introduction
Thermal desorption (TD) is a powerful and versatile sampling method for gas chromatography used for sample preparation and extraction. It allows a concentration enhancement of analytes by a factor of up to 106. In addition to sampling from air sample containers or online manifolds, TD-tubes are often used and desorbed into an inert carrier gas stream against the direction of loading [1], [2].
Conventional TD-tubes usually have inner diameters of several millimeters and contain 100 – 600 mg of adsorbent material, which ensures a high capacity for the analysis [1]. Large amounts of adsorbent and relatively thick tube walls come along with high thermal masses resulting in long desorption processes of typically 5–15 min for volatile organic compounds [3], [4], [5]. For analytes with high boiling points or low vapor pressures e.g. polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons desorption times are considerably longer [6], [7].
Due to the slow desorption of the primary sampling device and the associated broadening of analyte bands, a further concentration step with focusing traps is required prior to GC analysis. The desorbed analytes are refocused into a focusing trap at ambient or sub-ambient temperatures. Re-desorption takes place extremely fast with heating rates of up to 100 °C/s. This releases the analytes into a very small volume of carrier gas and thereby increasing the concentration enhancement factor and method sensitivity [1], [8].
In order to fully utilize the potential of hyper-fast GC measurements in combination with thermal desorption, it is necessary to considerably reduce the desorption time by significantly reducing the thermal mass and amount of adsorbent. For this purpose, a new thermal desorption unit (TDU) and new micro thermal desorption tubes (μTD-tubes) are developed. The μTD-tubes contain only 10 mg Tenax TA and have an outer diameter of only 1.6 mm.
Analytical separation is conducted with a flow-field thermal gradient gas chromatograph (FF-TG-GC). The functional principle of this GC was first published in 2015 by Boeker and Leppert [9]. Differences compared to conventional GC systems as well as the construction of a FF-TG-GC are explained in Chopra et al. [10].
In order to reduce the desorption time and to avoid the refocusing step, there have already been several approaches with microtraps [11], [12], [13], [14] and research regarding their characteristics in the past [15]. If the adsorbent quantity becomes too small, breakthrough can become a problem. However, it is not necessary to collect large quantities of sample in combination with the FF-TG-GC, as it works with thinner I.D. columns which have less sample loading capacity.
The objective of this study is the development of a low thermal mass TDU, that enables analytes to be desorbed very quickly. Proof-of-concept measurements were performed with an n-alkane mixture, including a calibration line, repeatability measurements, comparative tests of five different μTD-tubes and breakthrough experiments. Further aspects such as linear velocity, porosity, back pressure and full width at half maximum (FWHM) were also discussed.
2. Material and method
2.2. Instrumentation
2.2.1. Micro thermal desorption tubes (μTD-tubes)
μTD-tubes are made of stainless steel tubes with 1.6 mm O.D. and 1.4 mm I.D. (SWS Edelstahl GmbH & Co. KG, Emmingen-Liptingen, Germany). The tubes were cut into 8 cm long pieces and then deburred. Marking rings are engraved into the material to distinguish between the tubes. Subsequently, the tubes are cleaned with methanol and n-hexane, respectively, in an ultrasonic bath for 15 min. The μTD-tubes are filled with 10 mg of 80/100 mesh Tenax TA.
 Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1730: Fig. 1. Schematic drawing of the micro thermal desorption tube (μTD-tube). Loading and desorption of analytes occur in opposite directions. A - spring wire, B - volumetric mesh disk; C - Tenax-bed (10 mg); d - 1.6 mm O.D. and 1.4 mm I.D.
Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1730: Fig. 1. Schematic drawing of the micro thermal desorption tube (μTD-tube). Loading and desorption of analytes occur in opposite directions. A - spring wire, B - volumetric mesh disk; C - Tenax-bed (10 mg); d - 1.6 mm O.D. and 1.4 mm I.D.
Initially, some μTD-tubes were also filled with Tenax TA 60/80 mesh. However, measurements of the pressure drop across the Tenax packaging have shown that the variations between the μTD-tubes are greater with the coarser Tenax. For this reason, only μTD-tubes with Tenax TA 80/100 mesh were used in the present study.
In order to hold the Tenax-bed in place, 1 cm long as ‘U’-shaped spring wire pieces (0.4 mm diameter) and little disks (4 mm diameter) of a volumetric mesh (VG 230, GKD – Gebr. Kufferath AG, Düren, Germany) are placed in front of and behind the Tenax packaging (Fig. 1). The Tenax-bed is placed from 5 cm of the μTD-tube towards the lower end (loading side). 10 mg Tenax TA have an approximate length of 2 cm. Freshly filled μTD-tubes are then regenerated in a tube conditioner (TC-20, Markes International, Llantrisant, U.K.) under the following conditions: 2 h at 320 °C and 0.5 h at 335 °C with a nitrogen flow of 50 – 100 mL/ min. Since the tube conditioner is designed for conventional μTD-tubes with an outer diameter of 6 mm, it had to be previously modified for the μTD-tubes by the institute’s scientific workshop (Fig. S.1, Supplemental material).
2.2.2. Thermal desorption unit (TDU)
The TDU (HyperChrom Deutschland GmbH, Alfter, Germany) consists of two parts, the handpiece (1, Fig. 2) and the TDU base (2, Fig. 2). The μTD-tube (E) is inserted into the handpiece (1) and it is held by an O-ring as well as a sleeve and a grub screw (D). Via the bayonet lock (A1, A2) and further O-rings (C), the handpiece and the TDU base are connected gas-tight. Closing the bayonet lock automatically starts the measurement via a micro switch. Carrier gas is supplied through B1 and B2. F is the split outlet which can be optionally opened. A heating wire (H) is fixed at the injector tube (G), which is used to heat the TDU. The heating wire is electrically insulated with high-temperature insulating varnish. A thermocouple (I) for temperature control of the TDU is fixed at the center of the heat winding with a ceramic adhesive. To achieve the most even temperature distribution in the TDU, some sections of the stainless steel injector tube are additionally wrapped with aluminum foil. The heating is controlled by a microcontroller (Arduino Uno). A temperature profile along the injector tube (G) is given at different times after the start of heating to a set temperature of 250 °C in Fig. S.2 (Supplemental material). The TDU base is connected to the transfer line (K) by a modified 1/16” Swagelok connector (J). Both, the handpiece and the TDU base are placed into a 3D-printed polymer housing (M) in which two PC fans (L) are built-in for cooling. The use of plastic reduces the heat transfer from the permanently hot transfer line oven underneath (Fig. 3, B). The TDU base body, the tubings B2 and F as well as the components G and J (Fig. 2) are connected by laser welding.
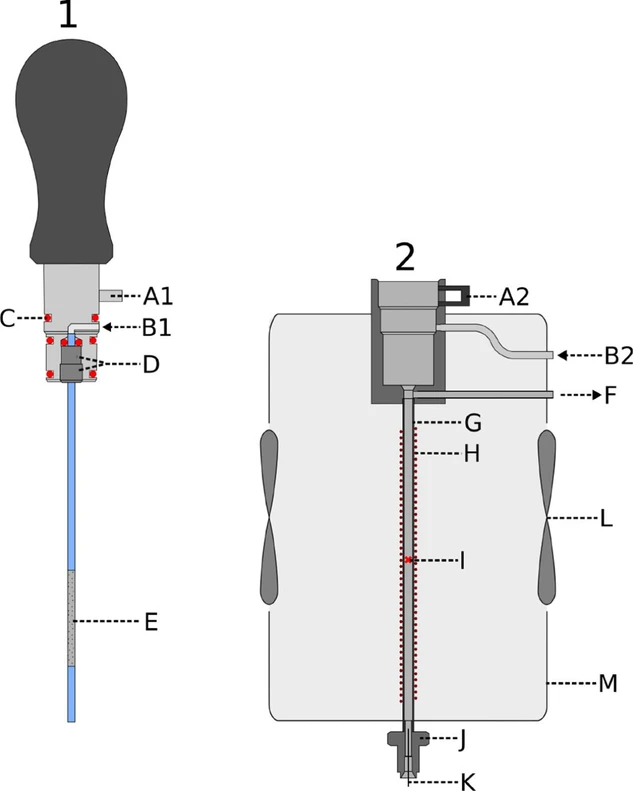 Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1730: Fig. 2. Schematic drawing of the thermal desorption unit (TDU). 1 - handpiece; 2 - TDU base; A - bayonet lock; B - carrier gas supply (Helium); C - O-ring; D - sleeve and grub screw for holding the μTD-tube; E - micro thermal desorption tube (μTD-tube) with Tenax-bed; F - split; G - injector tube; H - heat winding; I - temperature control point; J - transfer line connection; K - transfer line; L - PC fans; M - polymer housing.
Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1730: Fig. 2. Schematic drawing of the thermal desorption unit (TDU). 1 - handpiece; 2 - TDU base; A - bayonet lock; B - carrier gas supply (Helium); C - O-ring; D - sleeve and grub screw for holding the μTD-tube; E - micro thermal desorption tube (μTD-tube) with Tenax-bed; F - split; G - injector tube; H - heat winding; I - temperature control point; J - transfer line connection; K - transfer line; L - PC fans; M - polymer housing.
2.2.3. Flow-field thermal gradient GC (FF-TG-GC)
The FF-TG-GC (Fig. 3) setup is almost identical to the instrument described by Chopra et al. [10]. Instead of conventional GCs, an additively manufactured aluminum column fixture (Fig. 3, E) is now used, in which cooling channels are printed. The external water cooler (E200, Lauda, Lauda-Königshofen, Germany) stabilizes the measurement conditions and prevents a heating up of the column fixture (Fig. 3, E) due to heat radiation from the resistively heated capillary. Further, the water cooling allows a reduced cooling phase at the end of a measurement. The separation column temperature is set at the upper IR-sensor (Fig. 3, G). Unlike in Chopra et al. [10], the valve and sapphire nozzle for cryofocusing were not attached with an x-y-z linear translation stage, but can optionally be fixed directly to the GC housing via profile bars.
 Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1730: Fig. 3. Schematic drawing of the FF-TG-GC. A - TDU; B - transfer oven; C1/C2 - purged connectors; D - transfer line; E - column fixture; F - potential cryospot; G, H - upper and lower IR-sensor; I - resistively heated capillary; J - transfer oven; K - transfer line to the detector; L - FID a - carrier gas supply of the TDU (phase I); b - split; c - carrier gas supply of the purged connector C1 (phase 0, II and III), d - carrier gas supply of the purged connector C2.
Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1730: Fig. 3. Schematic drawing of the FF-TG-GC. A - TDU; B - transfer oven; C1/C2 - purged connectors; D - transfer line; E - column fixture; F - potential cryospot; G, H - upper and lower IR-sensor; I - resistively heated capillary; J - transfer oven; K - transfer line to the detector; L - FID a - carrier gas supply of the TDU (phase I); b - split; c - carrier gas supply of the purged connector C1 (phase 0, II and III), d - carrier gas supply of the purged connector C2.
4. Conclusion
The aim of this study was to optimize the desorption speed during thermal desorption in order to combine it efficiently with the fast measuring cycles of the FF-TG-GC. To this end, the thermal mass of both the TDU and the μTD-tube was drastically reduced compared to conventional TD tubes and desorption systems. By controlling the TDU, fixed heating ramps and holding phases are possible.
The new μTD-tubes have an inner diameter of 1.4 mm, a wall thickness of 0.1 mm and contain 10 mg Tenax TA. An alkane mixture from n-pentane to n-icosane could be desorbed in 12 s and separated by gas chromatography in a further 50 s. Including the cool down time of the system and the time required to insert a new μTD-tube, this results in a cycle time of approx. 90–100 s.
n-Octane to n-icosane were baseline separated. Coelution and possibly breakthrough occurred under the tested conditions between methanol, n-pentane, n-hexane and n-heptane. One possible solution to this problem is to purge the solvent methanol from the tube with air and to use additional cryofocusing to refocus the analytes at the head of the separation column.
The impact of the new μTD-tube dimensions on breakthrough, back pressure, porosity, linear velocity and FWHM was investigated and discussed. The optimized μTD-tube design showed promise in achieving faster desorption times while maintaining analytical precision.
In an upcoming contribution (part II), a method for the thermodesorption of explosives and civil warfare agent (CWA) simulants will be developed and validated.