News from LabRulezGCMS Library - Week 31, 2025

LabRulez: News from LabRulezGCMS Library - Week 31, 2025
Our Library never stops expanding. What are the most recent contributions to LabRulezGCMS Library in the week of 28th July 2025? Check out new documents from the field of the gas phase, especially GC and GC/MS techniques!
👉 SEARCH THE LARGEST REPOSITORY OF DOCUMENTS ABOUT GCMS AND RELATED TECHNIQUES
👉 Need info about different analytical techniques? Peek into LabRulezLCMS or LabRulezICPMS libraries.
This week we bring you posters by Agilent Technologies / ASMS, Shimadzu / ASMS, presentation by UCT / MDCW and other document by ALS Czech Republic!
1. Agilent Technologies / ASMS: Detection of VOCs by Agilent 8697 Headspace with 7010D GC/MS/MS Using Hydrogen Carrier Gas
- Poster
- Full PDF for download
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are present in the environment and can alter the chemistry of the atmosphere. Current methods for analyzing these compounds use gas chromatography with a single quadrupole detector and the sample is introduced using a purge and trap1 . With a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (GC/TQ) as a detector, we can acquire in dynamic MRM (dMRM) mode which enables lower detection levels by minimizing interference from coeluting compounds. Along with this TQ detector, we employed headspace as our sample introduction method and hydrogen carrier gas.
Experimental
Agilent 8890 GC with 8697 headspace and 7010D TQ was used for this analysis.A 20 m x 180 µm x 1 µm DB-624 column was used with a constant flow rate of 0.6 mL/min of hydrogen.
Conclusions
All 72 compounds successfully calibrated over multiple orders of magnitude using a combination of new techniques for VOC analysis.
- Hydrogen carrier gas does not drastically diminish sensitivity.
- The 7010D TQ in dMRM mode enables sensitivity to detect low ppb levels.
- Static headspace is a reproducible sample introduction technique for VOCs.
- Further method development may be necessary to improve peak shape of the gases.
2. ALS Czech Republic: Determination of Polychlorinated Naphthalenes in Solid and Aqueous Matrices
- Other document
- Full PDF for download
PCNs are a class of compounds in which hydrogen atoms are replaced by chlorine atoms in the naphthalene ring. In total, 75 congeners have been identified according to the number and position of the chlorine atoms (positions 1 to 8), their general formula is C10H8-nCln. Individual congeners differ in their degree of chlorination and physicochemical properties. Due to their persistence and toxicity, PCNs are considered to be significant environmental contaminants.
Due to their high thermal stability, hydrophobicity, and inertness, PCNs served as dielectric fluids in capacitors, insulating materials for wires and cables, wood preservatives, retardants, engine oil additives, and as raw materials for dye production. Estimated production of technical PCNs was 150,000–400,000 tons. Historical manufacturing and improper disposal represent significant sources of environmental contamination. Additionally, PCNs are formed as unintentional byproducts in various industrial processes, such as municipal solid waste incineration, iron ore sintering, secondary copper smelting, and other metallurgical operations. Even though the production and use of PCNs are now strictly regulated or banned, the legacy of early production and current unintentional releases has resulted in their detection across various environmental media and in food.
Human Health Risks Associated with PCNs
Exposure to PCNs has been linked to various adverse health effects, such as neurotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, immune suppression, and endocrine disruption, which can cause reproductive and developmental problems. Higher chlorinated PCNs, particularly hexachloronaphthalene, are especially toxic and may act similarly to dioxins. Due to their persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation, PCNs were added to the Stockholm Convention in 2015. Accurate quantification of PCNs emissions is essential for effective policy and risk management. Although global inventories are limited, recent studies identify key sources, including iron and steel production, waste incineration, and non-ferrous metal industries. New global emission inventories, using modeling methods and atmospheric transport analysis, are crucial for understanding PCNs distribution and guiding targeted reduction strategies to minimize environmental and health risks.
Determination of PCNs in ALS Laboratories
At ALS we use the most modern analytical method for the determination of PCNs that covers determination of chlorinated groups from monochloronaphthalenes to octachlorophthalenes and, if necessary, selected congeners (Table 1) in waste, aqueous and solid matrices.
For these purposes, we use gas chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry (GCHRMS) or gas chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry with a triple quadrupole (GC-MS/ MS). Both techniques use electron ionization and are based on the isotope dilution method using isotopelabeled standards, ensuring high accuracy and reliability of results. The developed method achieves limits of quantification defined by EU Regulation 2019/1021 on persistent organic pollutants, making it suitable for comparison of results with legislatively established limits.
3. UCT Prague / MDCW: Analysis of the human scent on the cartridge cases using GC×GC-MS/TOF
- Presentation
- Full PDF for download
This presentation explores an innovative forensic approach—identifying human scent signatures on spent cartridge cases using advanced analytical instrumentation. The study investigates whether scent could serve as a reliable alternative to traditional dactyloscopic (fingerprint) methods, especially when fingerprints are smudged or missing.
Analytical Technique
The scent analysis was carried out using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled with time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC×GC-TOF-MS), a powerful tool capable of detecting and resolving complex scent profiles.
Key Motivations
- Thermal Stability of Human Scent: Certain scent components, specifically ethyl esters of higher fatty acids, remain intact even after exposure to 500 °C for one minute—surviving firearm discharge.
- Complexity of Human Scent: Human scent consists of fractions of various volatility; less volatile compounds play a critical role in canine-based olfactory identification.
Pilot Study: Simulated Crime Scene
- 4 volunteers + 1 shooter
- 12 scent samples collected on glass beads and 4 unknown scent samples collected from cartridge cases
- Various surfaces: plastic, wood, concrete
Data Processing & Comparison
- Peak alignment using Kováts retention indices
- Selection of robust markers: present in ≥75% of volunteer samples and found on at least one cartridge
- Comparison based on area ratios of 150 lowest-variance substances
- Cluster analysis confirmed clear scent differentiation
Results & Conclusions
- Distinct scent profiles were successfully differentiated among individuals.
- Trained police dogs validated these findings by accurately matching samples.
- The type of surface (plastic, wood, concrete) on which the cartridge was found did not significantly affect scent retention or identification.
Future Directions
- Aligning analytical sensitivity between glass beads and cartridge cases.
- Reducing scent adsorption time on cartridges.
- Combining scent and fingerprint analysis from the same trace.
- Expanding to more volunteers, weapons, and ammunition types.
4. Shimadzu / ASMS: Multi-Residue Pesticide Analysis in Norbixin colour additive oleoresin using GC-MS/MS
- Poster
- Full PDF for download
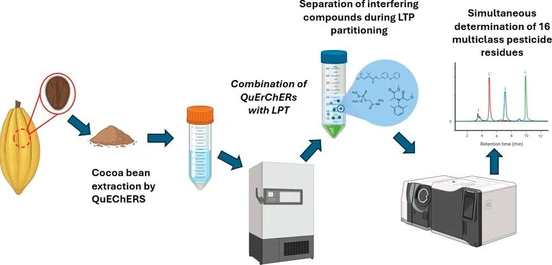
Norbixin is the yellow-(red) orange carotenoid, which in combination with bixin, constitutes for 80% of red-orange annatto dye. It is extracted from the pericarp of the seeds of Bixa Orellana (Figure 1). The annatto pigment has global economic significance, as it is one of the most widely used natural dyes to color food, cosmetics and pharmaceutical products
Owing to its large culinary uses and other diverse applications, use of chemical pesticides for its production in large quantities is imperative. Dye extraction process may result in concentration of pesticides and in turn contribute to adverse impact on human health when incorporated in various preparations. Hence quantitation of residual pesticides in norbixin colour additive becomes very important. As the oleoresin is a complex matrix for extraction, it is required to develop a rugged, sensitive and efficient method for residual pesticide analysis.
This study reports a highly sensitive method for simultaneous quantification of multiple pesticides in complex matrix of norbixin using modified QuEChERS[1] with triple quadrupole gas chromatography (GC-MS/MS) system. GCMS-TQ8040 NX, manufactured by Shimadzu Corporation Japan, was used to quantify residual pesticides in Norbixin oleoresin sample
Conclusion
- This study shows that the modified QuEChERS method combined with GC-MS/MS system is a reliable and efficient tool to quantify residual pesticides in norbixin sample. Although oleoresin is a complex matrix, the modified QuEChERS method significantly reduces interference.
- Also, highly sensitive Shimadzu GC-MS/MS allows trace level detection even after multifold dilution of sample. This helps in reducing contamination and enhancing ruggedness resulting in reproducible detection of analytes.
- The combination of sensitive instrument and reliable method enables its use in testing laboratories for multi-residue analysis of Norbixin oleoresin.