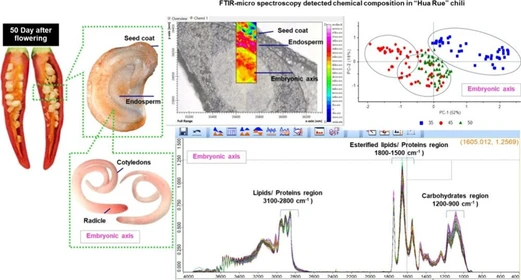
More Analyses, Less Helium! Helium Savings in Gas Chromatography: Watrex Helium Saver™

Watrex Prague: More Analyses, Less Helium! Helium Savings in Gas Chromatography: Watrex Helium Saver™
Gas chromatography (GC) is a key analytical technique widely used in chemical, pharmaceutical, and food laboratories. Especially in combination with mass spectrometry (GC/MS), it represents an indispensable tool for qualitative and quantitative analysis of trace compounds. One of the limiting factors of this method, however, is the consumption of carrier gas – traditionally helium.
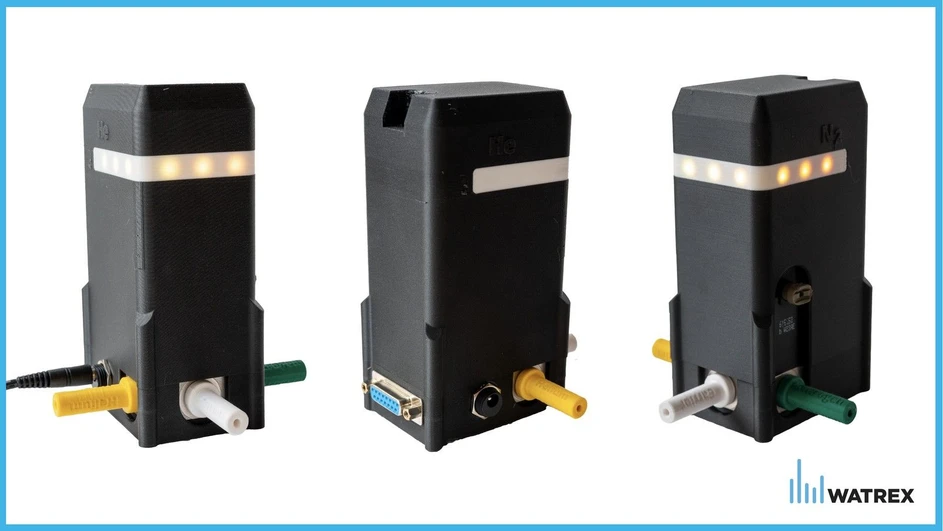
 Watrex: Fig. 1 Watrex Helium Saver™
Watrex: Fig. 1 Watrex Helium Saver™
Why Helium?
Helium is preferred in gas chromatography due to its inertness, low density, and excellent separation capabilities, particularly in GC/MS where other gases (e.g., nitrogen) do not achieve the required sensitivity and separation speed. Hydrogen could serve as an alternative, but it comes with safety risks (flammability and explosiveness) and, in some applications, chemical reactivity, which may affect the results.
Interestingly, helium, although the second most abundant element in the universe, is rare and non-renewable on Earth. It is produced as a by-product of alpha decay of heavy elements and naturally escapes into space. It is often obtained as a by-product of natural gas extraction. Due to growing demand and limited reserves, prices are steadily increasing – currently, a single cylinder can cost CZK 20,000–80,000, with typical laboratory consumption lasting only 1–2 months.
How Do Laboratories Save Helium?
Switching to Hydrogen as Carrier Gas
Hydrogen (H₂) is used in some laboratories as an alternative to helium due to its availability and lower cost. However, it has several significant drawbacks:
- Safety risk: Hydrogen is highly flammable and explosive, requiring strict safety measures, leak detectors, and proper ventilation.
- Chemical reactivity: Unlike helium, it is not completely inert. It can react with some analytes or column materials, leading to chromatographic artifacts and distorted results.
- Limited method compatibility: Switching to hydrogen often requires re-validation of methods, changes in separation conditions, and detector adaptation. Not all methods are suitable for this transition, and the process may be time-consuming and costly.
Switching to Nitrogen Outside Measurement Periods
Nitrogen (N₂) is a cheap, available, and inert gas that can be used to purge chromatographic systems when no measurements are being performed. This helps conserve helium during instrument downtime. However, this method has several limitations:
- Manual switching required: Operators must switch gases manually and ensure correct timing. Forgetting to switch may lead to either helium waste or delays in starting analyses.
- Purge time: Before each measurement, the system must be flushed with helium to remove nitrogen and ensure proper chromatographic conditions. This can prolong startup times.
- Limited efficiency: Even with diligent manual switching, some helium is still wasted, especially if the operating mode changes frequently.
Watrex Helium Saver™: Automated Helium Savings
Watrex Praha has introduced Helium Saver™, an intelligent device that addresses this problem fully automatically.
- How it works: The device monitors the operating schedule of the chromatograph, automatically switches between helium and nitrogen according to the defined plan, and ensures sufficient helium purging before analysis.
- Helium savings: During idle periods, the instrument runs on nitrogen, reducing helium consumption by significant percentages.
- Easy configuration: The device connects via USB – it appears as a flash drive, and all adjustments can be made using any text editor without the need for special software.
- Universal compatibility: It can be easily integrated into any GC/MS system thanks to its universal interface.
- Safety and simplicity: Both automatic and manual modes are available, eliminating the need for daily manual switching.
 Watrex: Fig. 2 Watrex Helium Saver™
Watrex: Fig. 2 Watrex Helium Saver™
Benefits for Laboratories
Implementing Helium Saver™ brings:
- significant cost savings,
- improved operational safety,
- a more sustainable approach to scarce resources,
- simplified configuration and installation,
- optimized laboratory downtime management.
Conclusion
Helium remains an essential carrier gas in gas chromatography, particularly in GC/MS applications. With rising costs and limited availability, efficient helium management is becoming increasingly important. Watrex Helium Saver™ offers a practical, flexible, and fully automated solution that allows laboratories to use helium more efficiently, without compromising analytical quality.
Contact us for more information or a non-binding quote at [email protected].